Research Study
Children with cerebral palsy
Combined passive stretching and active movement rehabilitation of lower-limb impairments in children with cerebral palsy using a portable robot.
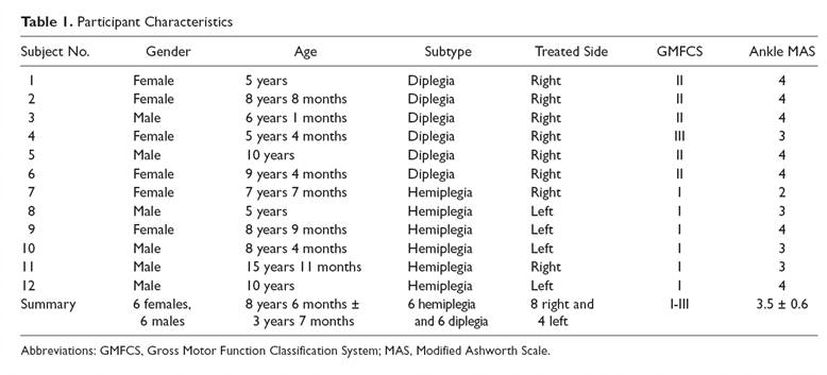
Participant Characteristics

All participants completed 18 sessions of training with significant improvements:
Passive stretching was able to relax the stiff muscles: ↑ PROM
↑ Motor control: ↑ AROM , ↑ strength and ↑ SCALE may be due to better control after muscles became less stiff
Biofeedback game-playing and repetition (motor learning)
Improvement of selective motor control also seen in foot and hip
Strengthening adopted in the study did not increase spasticity
Muscle Improvement
Measurable changes of Calf Muscle-Tendon Properties Induced by Stretching and Active Movement Training in Neurological Impairment
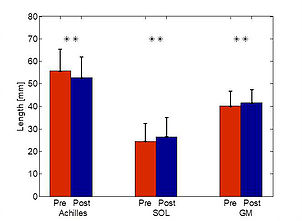
Muscle Length Improvement:
-
SOL fascicles from 24.8±8.2 to 26.8±8.6 mm (**)
-
GM fascicles from 40.2±6.6 to 41.5±5.9 mm (**)
-
Achilles tendon from 55.7±9.9 to 52.6±9.4 mm (**)
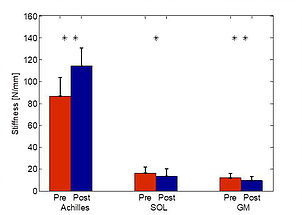
Muscle Stiffness Improvement
-
SOL fascicular stiffness from 16.6±5.2 to 13.8±6.3 N/mm (*)
-
GM fascicular stiffness from 12.2±3.8 to 9.6±3.6 N/mm (**)
-
Achilles tendon stiffness from 86.8±16.9 to 114.4±16.0 N/mm (**)
Research References
-
Combined passive stretching and active movement rehabilitation of lower-limb impairments in children with cerebral palsy using a portable robot. Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repair. 25, 378-385, 2011.
-
Changes of Calf Muscle-Tendon Properties Induced by Stretching and Active Movement Training in Neurological Impairment. Journal of Applied Physiology, 111(2), 435-442, 2011
-
Reliability of the intelligent stretching device for ankle stiffness measurements in healthy individuals. The Foot 20 (2010) 126–132
-
Does acute passive stretching increase muscle length in children with cerebral palsy? Clinical Biomechanics 28 (2013) 1061–1067
-
Responses to static stretching are dependent on stretch intensity and duration. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. 2014 Aug 27. doi: 10.1111/cpf.12186.
-
(Sukal-Moulton, T., Clancy, T., Zhang, L.-Q., and Gaebler-Spira, D.)Clinical application of a robotic ankle training program for cerebral palsy compared to the research laboratory application: Does it translate to practice? Arch Phys Med Rehab. 95, 1433-1440, 2014.
